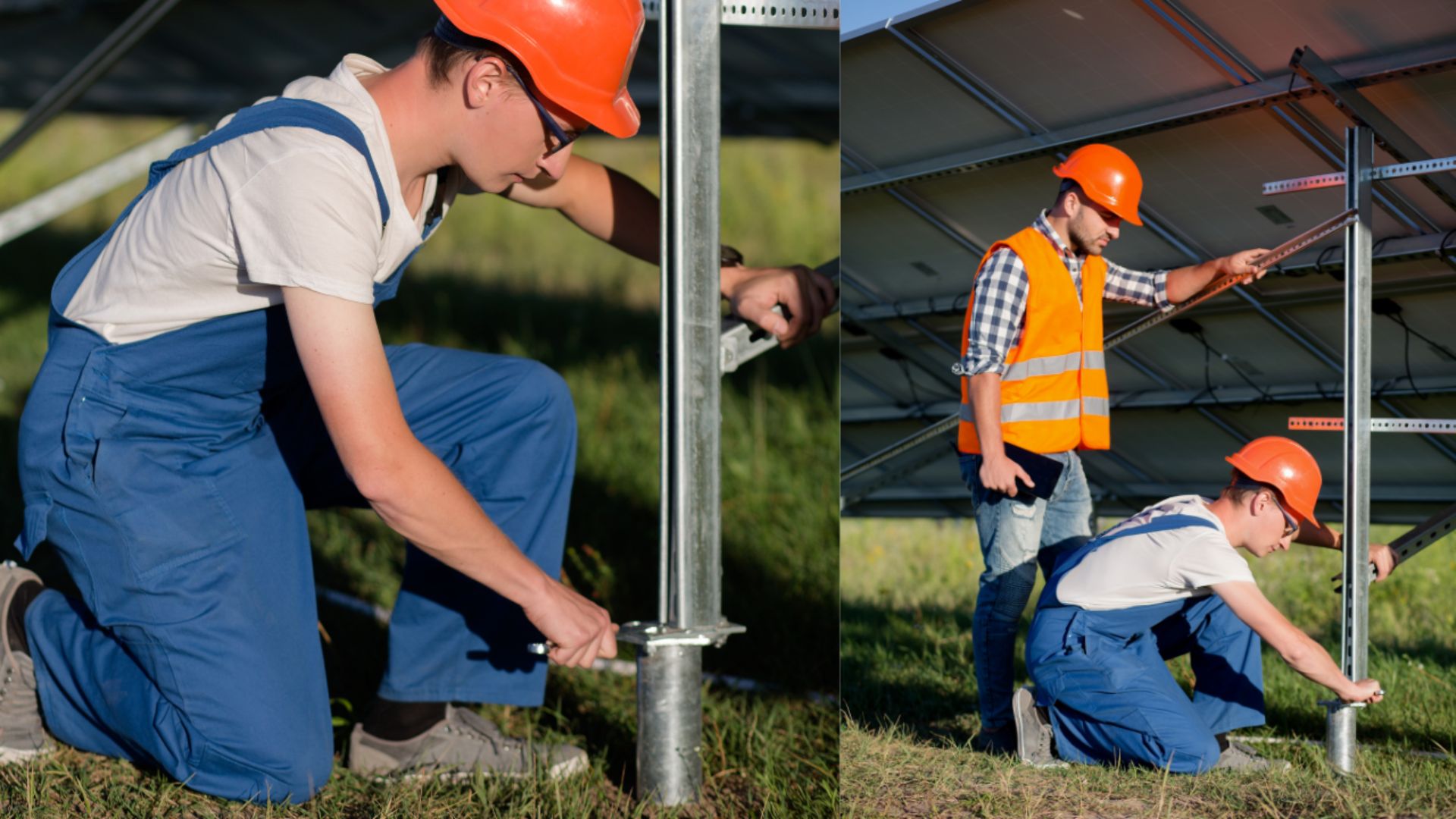
If you are in the construction industry, you may have heard of the term “helical pile.” But what exactly is a helical pile, and why is it used?
In this blog post, we will provide you with an in-depth guide on what a helical pile is, the different types of helical piles available in the market, and their applications.
What is a Helical Pile and How Does it Work?
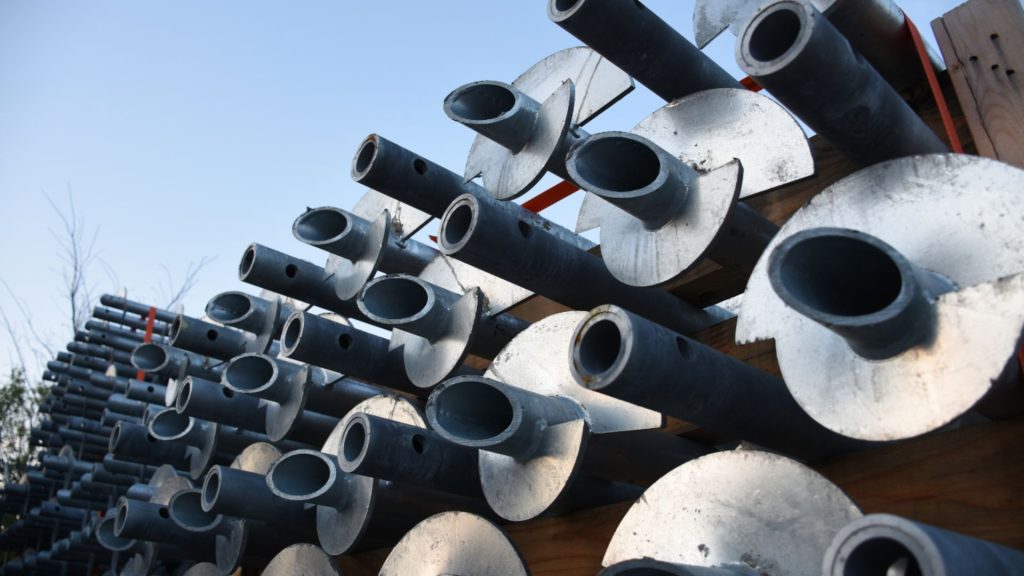

A helical pile is a foundational device used to support structures built on soil that lacks the required bearing strength. It is made up of multiple shafts that are screwed into the ground to create a stable support system.
Helical piles are often used as an alternative to traditional foundation techniques like concrete cast-in-place pillars, drilled piers, and driven piles.
There are different types of helical piles available, each with a unique design that makes it suitable for different soil conditions and construction projects.
Shaft material, size, and helix spacing all impact the design of a helical pile. Some common types of helical piles are square bar piles, round shaft piles, and pipe piles.
Square bar piles are designed to penetrate hard soils, while round shaft piles are used to support light structures. Pipe piles are designed to support large compressive loads and tension loads. Understanding the soil conditions is key to selecting the appropriate type of helical pile.
The application of helical piles is diverse. Helical piles are ideal for supporting light structures like prefabricated homes, flagpoles, decks, and sheds. They are also used in larger applications such as towers, bridges, and transmission lines. Their adaptability makes them useful in both commercial and residential construction projects.
Helical piles offer numerous advantages over traditional foundation techniques, including the fact that they are cost-effective, can be installed quickly, and can be easily customized. They are often installed using a hydraulic motor attached to excavators or skid steers, making the installation process quicker and more efficient.
What is the History of Helical Piles?
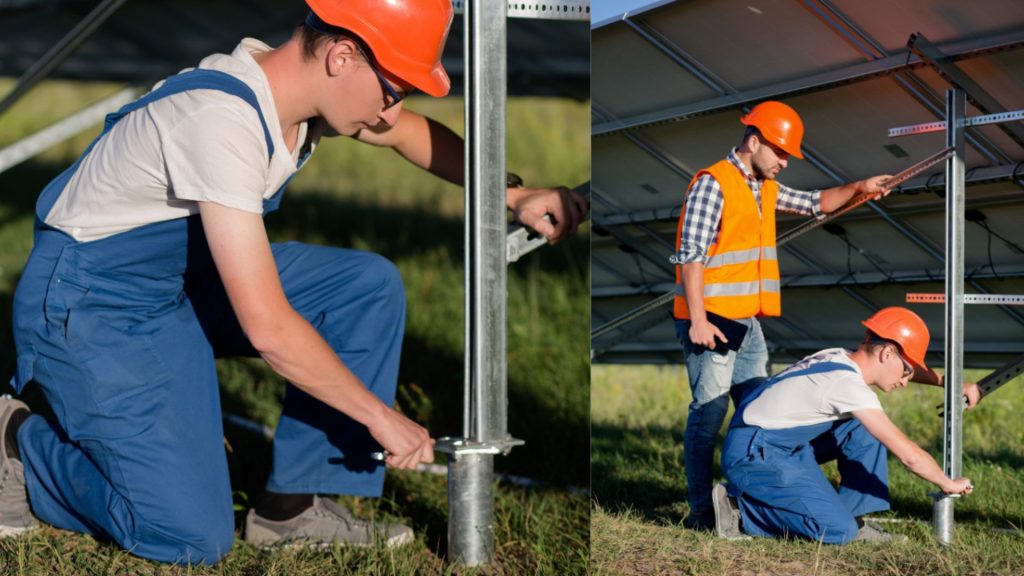

Helical piles have been used in construction projects for many years, with a history dating all the way back to the 1830s when they were first used to stabilize lighthouse foundations in England.
Over time, they have become increasingly popular due to their ease of installation, versatility, and ability to provide strong support even in challenging soil conditions.
Helical piles are essentially long, steel shafts that feature one or more helix-shaped plates near the end. These plates help to anchor the pile in place and provide increased stability as weight is placed on the pile.
Today, they are used in a wide range of applications, including residential and commercial construction, bridge and roadway support, and even for wind turbines and solar panels.
As such, they have become a vital component of modern construction and engineering projects.
How are Helical Piles Designed?
Helical piles have become an increasingly popular choice for building foundations due to their excellent performance, reliability, and ease of installation.
But how exactly are these innovative structures designed? Helical piles are typically engineered and customized based on the specific soil conditions at the construction site.
The design process involves careful calculations of factors like the soil type, depth and consistency, and the loads the pile will be required to support.
Sophisticated software tools and specialized equipment are used to precisely measure and analyze these factors, which ultimately inform the design of the pile’s size, shape, and helix configuration.
It’s a complex process requiring years of engineering expertise, but ultimately producing a foundation that is durable, robust, and built to last for decades to come.
What are the Different Types of Helical Piles?
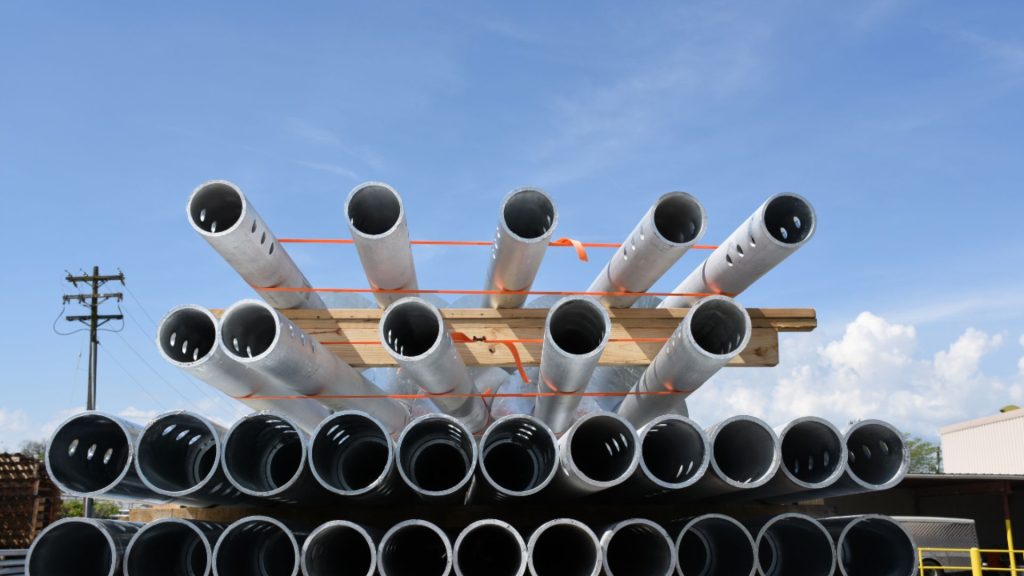

Helical piles are a great foundation option for structures built on unstable soils. They are typically made from steel and consist of a helix – a spiral-shaped plate – that is attached to a central shaft.
There are several types of helical piles, including segmental, sectional, and continuous flight auger (CFA) piles.
Segmental helical piles are made from a series of sections that fit together, much like a screw. Sectional piles, on the other hand, are made from multiple sections that are welded together.
CFA piles are created by drilling a hole into the ground and then twisting the pile into the soil as the hole is filled with concrete. No matter what type of helical pile is used, they all offer a cost-effective, efficient, and long-lasting solution for foundation concerns.
Installation Process for Helical Piles
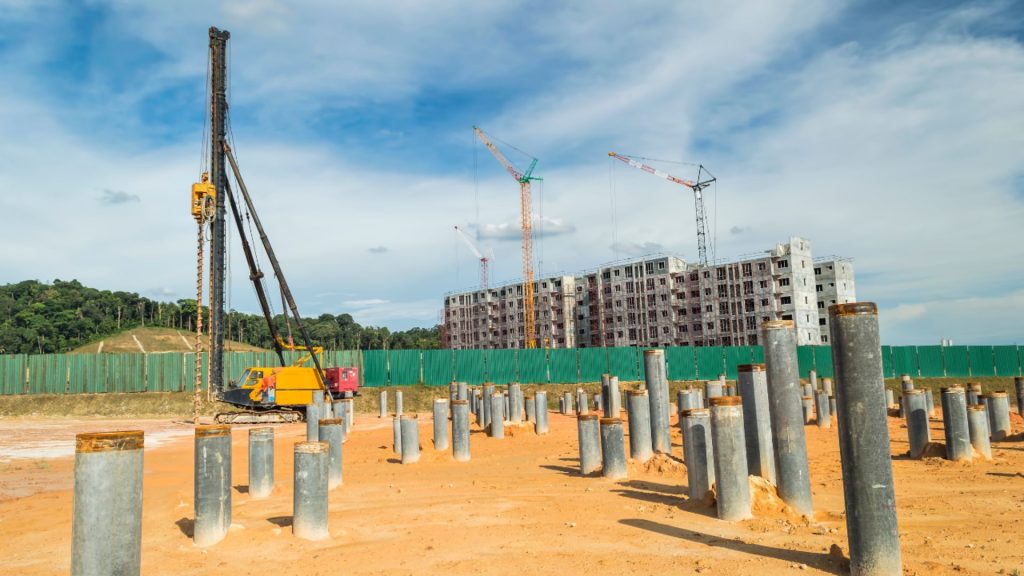

Sure, there’s an installation process for helical piles in listicle format:
- Soil Analysis: Analyze soil type and bearing capacity of the site.
- Equipment Preparation: Gather all necessary equipment, including a hydraulic torque motor, helical piles, and extensions.
- Digging Holes: Using a small excavator, dig holes for each pile location.
- Insert Piles: Insert the helical piles into the holes using the torque motor to ensure they are securely anchored.
- Add Extensions: If needed, add extensions to the piles to achieve the proper depth.
- Verify the Level: Use a level to ensure that each pile is installed vertically.
- Connect to Foundation: Attach foundation brackets to the piles, which support beams and connect them to the foundation.
- Load Testing: Perform a load test to verify the capacity of the piles.
- Backfilling: Backfill the holes with dirt to complete the installation.
10 Benefits of Using Helical Piles

1. Easy and Fast Installation:
Helical piles can be installed quickly and easily without generating as much noise or vibration as other installation methods.
2. Cost-Effective:
Compared to traditional foundation methods, helical piles are more cost-effective and require less labour and equipment.
3. Versatile:
Helical piles can be used in a wide variety of soil conditions and can be installed at any angle.
4. Environmentally Friendly:
Helical piles do not require the use of harmful chemicals or heavy equipment, which makes them an environmentally friendly solution for foundation work.
5. High Load Capacity:
Helical piles have a high load capacity, which means they can support heavy structures with ease.
6. Customizable:
Helical piles can be customized to fit a wide range of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial projects.
7. Predictable Performance:
Helical piles are designed to provide predictable and reliable performance, which reduces the risk of foundation failure.
8. Low Maintenance:
Once installed, helical piles require very little maintenance, which means you won’t have to worry about costly repairs or replacements.
9. Can Be Installed in Tight Spaces:
Helical piles can be installed in tight spaces where traditional foundation methods are not feasible.
10. Long-lasting:
Helical piles are made from durable materials that can withstand harsh weather conditions, which means they can last for decades without needing to be replaced.
5 Advantages and Disadvantages of Installing a Helical Pile
Advantages of Installing a Helical Pile
- Easy and fast installation process
- Versatility – can be installed in various soil conditions
- High load-bearing capacity
- Environmentally friendly
- Requires less excavation compared to other foundation methods
Disadvantages of Installing a Helical Pile
- Cost – While helical piles can be cost-effective, it is still more expensive than some traditional foundation methods.
- Depth limitations – Helical piles might not penetrate deep enough into the soil to support heavy loads or larger structures.
- Limited availability of professionals – Helical piles requires experienced and skilled professionals for proper installation, which could limit the number of available installers.
- Dependence on soil conditions – Helical piles’ performance is highly dependent on the soil conditions. If the soil conditions are poor, the helical piles may not provide the necessary strength and stability.
- Risk of corrosion – In some cases, helical piles may be at risk of corrosion, which could lead to structural damage over time if not properly maintained.
5 Common Uses for Helical Piles in Construction Projects
Helical piles have been gaining popularity in recent years as versatile and reliable foundation solutions for various construction projects.
Here are 5 common uses for helical piles in construction projects:
1. Foundation Support:
Helical piles are used as a foundation support solution for new building construction, including residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. The piles are driven into the soil using specialized equipment and can provide strong, stable support for the structure. Helical piles are beneficial in that they can be installed quickly and easily and can be customized to fit the specific needs of the project.
2. Soil Stabilization:
Soil stabilization is another common use for helical piles. In some cases, soil conditions may be unstable or unsuitable for traditional foundation methods. Helical piles can be used to stabilize the soil and provide a secure foundation for structures. This application is especially useful for infrastructure projects, such as bridges and highways, where soil stability is critical.
3. Retaining Walls:
Retaining walls are commonly used in construction projects to prevent erosion and stabilize slopes. Helical piles can be used to support retaining walls, particularly in areas with difficult access or where traditional construction methods are not feasible. Helical piles can be used to anchor retaining walls in place and provide additional stability.
4. Solar Panel Installation:
Helical piles are also used for solar panel installation. Solar panels require a stable foundation, and helical piles provide a cost-effective and efficient solution. Helical piles are driven directly into the ground, providing a solid foundation for solar panels. They can be installed quickly and easily, which makes them an ideal foundation solution for solar panel installation.
5. Boardwalks and Decks:
Boardwalks and decks require a stable foundation to ensure safety and longevity. Helical piles are used in these applications to provide a stable foundation for the structure. Helical piles can be installed in various soil conditions and can be customized to fit the specific needs of the project. This application is particularly useful in areas with high water tables or where traditional foundation methods are not feasible.
In conclusion, helical piles are a versatile and reliable solution for various construction projects.
10 Tips on Choosing the Right Size and Type of Helical Pile for Your Project

Choosing the right size and type of helical pile is critical to the success of any construction project. Here are 10 tips on how to choose the right size and type of helical pile for your project:
1. Soil Analysis:
Before choosing a helical pile, you should conduct a soil analysis. The soil conditions at your project site will have a significant impact on the type and size of the helical pile you need. Soil analyses will identify the soil type, bearing capacity, and other factors that will influence the helical pile’s performance.
2. Load Capacity:
The size of a helical pile is determined by the load capacity required for your specific project. Engineering calculations based on the soil analysis will help determine the appropriate size of the helical pile needed to support the weight of the structure.
3. Type of Helical Pile:
There are different types of helical piles, each designed for specific applications. For example, round shaft piles are used for compression loads, while square shaft piles are used for tension loads. Screw piles are designed for smaller structures and lighter loads, while helical anchors are used in soil stabilization projects. It’s important to choose the right type of helical pile for your specific project needs.
4. Environmental Factors:
Environmental factors such as temperature, moisture, and the presence of corrosive materials can also affect the choice of the helical pile. In areas with high levels of corrosion, stainless steel or galvanized steel piles may be necessary.
5. Installation Method:
The installation method you choose will also determine the type and size of the helical pile required. For example, if you’re installing a pile in tight spaces or around existing structures, you may need a smaller pile with a more compact installation method.
6. Project Budget:
The cost of helical piles can vary greatly depending on the size and type of pile needed for your project. It’s important to choose a pile that meets your project requirements while also staying within budget.
7. Contractor Experience:
It’s important to work with a contractor that has experience installing helical piles. A qualified contractor will have the knowledge and expertise to choose the right size and type of helical pile for your project and ensure proper installation.
8. Building Codes:
9. Project Timeline:
Building codes and regulations may also dictate the size and type of helical pile required for your project. It’s important to consult with local building authorities and ensure that you are following all necessary codes and regulations.
The timeline for your project can also impact the choice of the helical pile. Some types of piles may require longer installation times or may not be available within the desired timeframe. It’s important to consider the project timeline when selecting the right size and type of helical pile.
10. Maintenance Requirements:
Finally, it’s important to consider the maintenance requirements of the helical pile. Some piles may require regular maintenance or monitoring to ensure their continued performance. It’s important to choose a pile that meets your maintenance needs and fits within your project budget.
In conclusion, choosing the right size and type of helical pile is critical to the success of any construction project. A soil analysis, load capacity, type of helical pile, environmental factors, installation method, project budget, contractor experience, building codes, project timeline, and maintenance requirements must all be considered when making this important decision. By taking the time to carefully evaluate these factors, you can ensure that you choose the right helical pile for your project and avoid potential issues down the road.
FAQ’s
What is a helical pile?
A helical pile, also known as a screw pile or helical anchor, is a deep foundation system consisting of a steel shaft with helical-shaped plates (or helices) attached to it. These helices enable the pile to be advanced into the ground by twisting or screwing it in, providing load-bearing capacity and stability.
How do helical piles work?
Helical piles work on the principle of helical plates bearing into the soil to generate support and resistance. During installation, the pile is rotated into the ground using hydraulic machinery or other suitable equipment. The helical plates cut into the soil, creating a helical path that helps distribute the structural loads along the pile shaft, ultimately providing stability for the foundation.
Where are helical piles commonly used?
Helical piles are versatile and can be used in various construction projects. They are commonly employed in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Helical piles are often used for building foundations, underpinning existing structures, supporting retaining walls, stabilizing slopes, and for applications in deep foundation systems where traditional foundations are impractical.
What are the advantages of using helical piles?
Helical piles offer several advantages over traditional foundation systems. They can be installed quickly with minimal equipment and vibration, making them suitable for projects with time and space constraints. Helical piles also provide immediate load-bearing capacity, reducing the need for waiting periods. They are versatile and can be used in various soil conditions, including soft soils and areas with high water tables.
Can helical piles be removed or adjusted if needed?
Yes, helical piles can be removed or adjusted if necessary. One of the key benefits of helical piles is their versatility and ease of installation/removal. If a pile needs to be repositioned or removed, it can typically be unscrewed from the ground using the same equipment used for installation. This flexibility makes helical piles a convenient choice for temporary structures or situations where adjustments may be required.
What is the difference between a screw pile and a helical pile?
The terms “screw pile” and “helical pile” are often used interchangeably, as they refer to the same type of deep foundation system. Both screw piles and helical piles consist of a steel shaft with helical-shaped plates attached to it. The helical plates enable the pile to be screwed or twisted into the ground. So, in essence, there is no significant difference between the two terms.
What are helical piles made of?
Helical piles are typically made of high-strength steel. The steel shaft is usually manufactured using seamless tubing or solid steel bar, while the helical plates are made of thick steel plate material. The steel used in helical piles is chosen for its strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, ensuring the stability and longevity of the foundation system.
What is the size of the helical pile?
The size of a helical pile can vary depending on the specific engineering requirements of a project. The size of a helical pile is typically determined by factors such as the expected loads, soil conditions, and design specifications. Helical piles come in various diameters and lengths, ranging from a few inches to several feet in diameter and from a few feet to tens of feet in length.
Why are helical piles used?
Helical piles are used for several reasons. They are an effective solution for providing load-bearing capacity and stability in various soil conditions, including soft soils, clay, sand, and areas with high water tables. Helical piles are often used to support structures and foundations, stabilize slopes and embankments, and resist uplift and lateral forces. They offer advantages such as ease of installation, immediate load-bearing capacity, and minimal site disturbance.
What is the maximum spacing of helical piles?
The maximum spacing of helical piles depends on factors such as the design loads, soil conditions, and the structural requirements of the project.
The spacing between helical piles is typically determined by a geotechnical engineer or a structural engineer based on the specific site conditions and load calculations. It is crucial to ensure proper spacing to distribute the loads effectively and maintain the stability and integrity of the foundation system. The maximum spacing can vary and should be determined on a case-by-case basis by a qualified engineer.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, helical piles are a crucial component in modern construction projects. They provide a cost-effective solution to stabilizing buildings and structures in areas with poor soil conditions.
As outlined in this guide, there are several types of helical piles available, each designed to cater to specific soil types and construction projects.
The advantages of using helical piles over traditional foundation techniques make them a valuable asset to the construction industry.
You May also like:
What are building foundations
Understanding Gravity Load In Building Construction
What are Beams and Columns in Structural Engineering?
Best Tablets For Civil Engineers
Best Tablets For Structural Engineers
Best Laptops For Civil Engineers
Best Laptops For Structural Engineers